The advantages of multi-target speed radar in speed measurement applications
With the rapid development of intelligent transportation systems, the application of radar technology in traffic management is becoming increasingly widespread. Among them, speed radar, as an important tool for traffic law enforcement, can not only monitor the speed of vehicles on the road in real time, but also regulate traffic behavior to a certain extent and reduce the occurrence of traffic accidents. According to their different functions and technologies, speed radar can be roughly divided into two categories: multi-target speed radar and single lane speed radar. This article aims to explore the differences between these two types of radar and their respective application scenarios.
Single lane speed radar is typically designed to monitor the speed of vehicles on a single lane. This type of radar is compact, easy to install, and cost-effective. The radar uses the Doppler effect to detect vehicle speed, and the checkpoint speed measurement and capture system composed of camera triggered photography and image data processing modules has been favored by the market due to its simple structure, easy installation, good environmental adaptability, and stability. In addition, this type of radar does not require additional lights when triggered at night, does not affect the driver’s line of sight, and is easy to construct and maintain, with significantly lower costs compared to ground sensing coils.
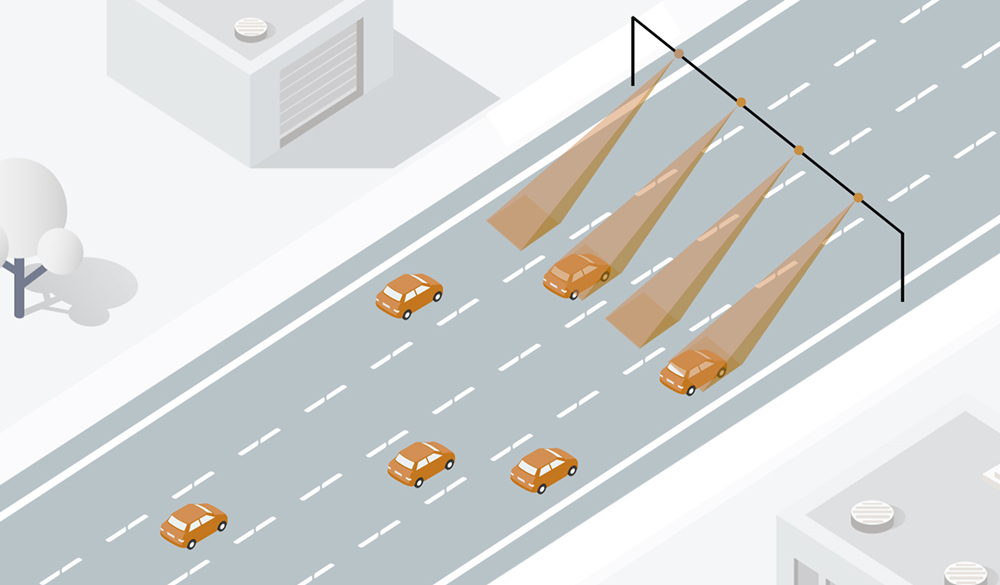
In contrast, multi-target speed radar has more advanced technology and higher performance indicators. It can simultaneously detect multiple vehicle targets on multiple lanes and distinguish between incoming and outgoing vehicles, making it suitable for complex traffic environments. Multi target speed radar can not only achieve multi lane coverage on highways, but also effectively avoid interference between adjacent lanes, achieving high-precision detection of speeding vehicles. Multi target speed radar can simultaneously monitor more than 4 lanes and provide vehicle speed, distance, and lane information, improving the integration of each lane checkpoint system and achieving accurate speed measurement of vehicles in each lane.
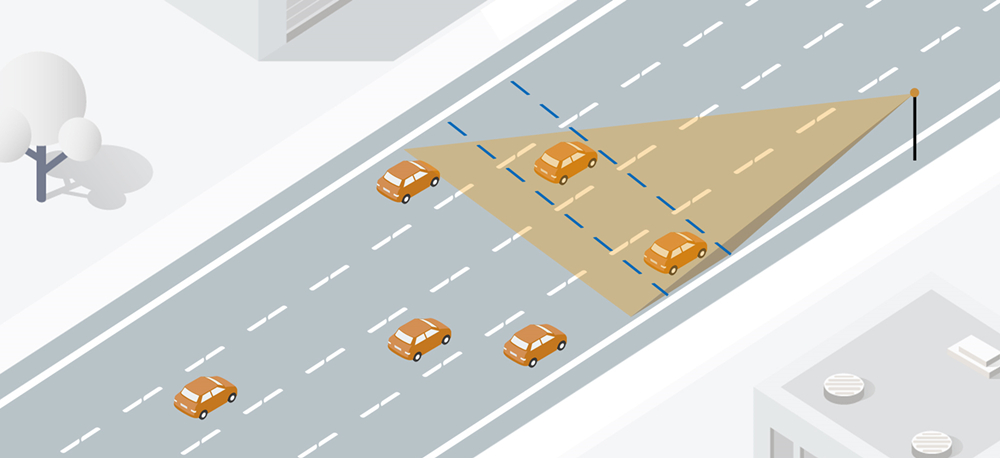
From a technical perspective, the biggest difference between multi-target speed radar and single lane speed radar lies in their processing capability and coverage range. Multi target speed radar often adopts more complex data processing algorithms, such as the multi-target detection method based on FMCW millimeter wave radar and the multi-target recognition algorithm based on improved LFMCW radar, which enable it to handle complex multi-target scenes. Single lane speed radar, on the other hand, places greater emphasis on simplifying its design to ensure stable and reliable operation in specific environments.
In terms of application scenarios, single lane speed radar is suitable for simple traffic monitoring situations, such as speed measurement on urban or rural roads. Such situations often have low traffic flow and do not require particularly complex radar systems. Multi target speed radar is more suitable for applications in places with high traffic volume and high requirements for vehicle monitoring accuracy, such as highways, graded highways, and intercity highways. In addition, multi-target speed radar can also be used for speed measurement in accident prone road sections, capturing emergency lane occupancy on highways, and so on.
Although multi-target speed radar is more expensive, it may be more cost-effective in terms of overall project cost as it can cover multiple lanes simultaneously, reducing the number of radars that need to be deployed. In contrast, if a single lane speed radar is used to cover the same multi lane area, separate radar devices need to be installed in each lane, which not only increases the cost of equipment procurement but also leads to higher installation costs. In addition, in terms of subsequent maintenance, the need for multiple single lane speed sensors for multiple lanes means more maintenance points, increasing the complexity and cost of maintenance. Multi target speed measurement radar, due to being concentrated on one or more devices, is relatively easy to maintain and the overall maintenance cost will be correspondingly reduced. Therefore, when considering long-term operating costs and ease of maintenance, a multi-target speed radar may be a more cost-effective option.
Multi target speed radar provides more flexible installation options due to its ability to simultaneously monitor multiple lanes. It can be installed above the road or on the roadside, reducing dependence on road structures and facilitating deployment in different road environments. Single lane speed radar usually needs to be installed directly above the lane, which not only limits the choice of its installation location, but may also require additional structural support, such as beams or brackets, increasing the complexity and cost of installation. Therefore, when considering installation convenience and impact on existing infrastructure, multi-target speed radar exhibits higher flexibility and adaptability.
