Unlocking Precision and Safety with Long Range Radar Sensor
In an era defined by automation and intelligent systems, Long Range Radar Sensor have become indispensable across industries that depend on precise detection and situational awareness. From managing complex traffic systems to securing critical infrastructure and enabling autonomous driving, these sensors are transforming how the world perceives, reacts, and operates in real time.
Unlike optical cameras or infrared systems, radar sensors work reliably in all weather, lighting, and visibility conditions. They can detect and track multiple objects at long distances — sometimes beyond 300 meters — with remarkable accuracy. This makes them essential in applications where reliability and safety cannot be compromised.
Below, we’ll explore how Long Range Radar Sensors solve real-world problems in three key domains: transportation systems, perimeter security, and autonomous driving.
1. Traffic Management and Intelligent Transportation Systems
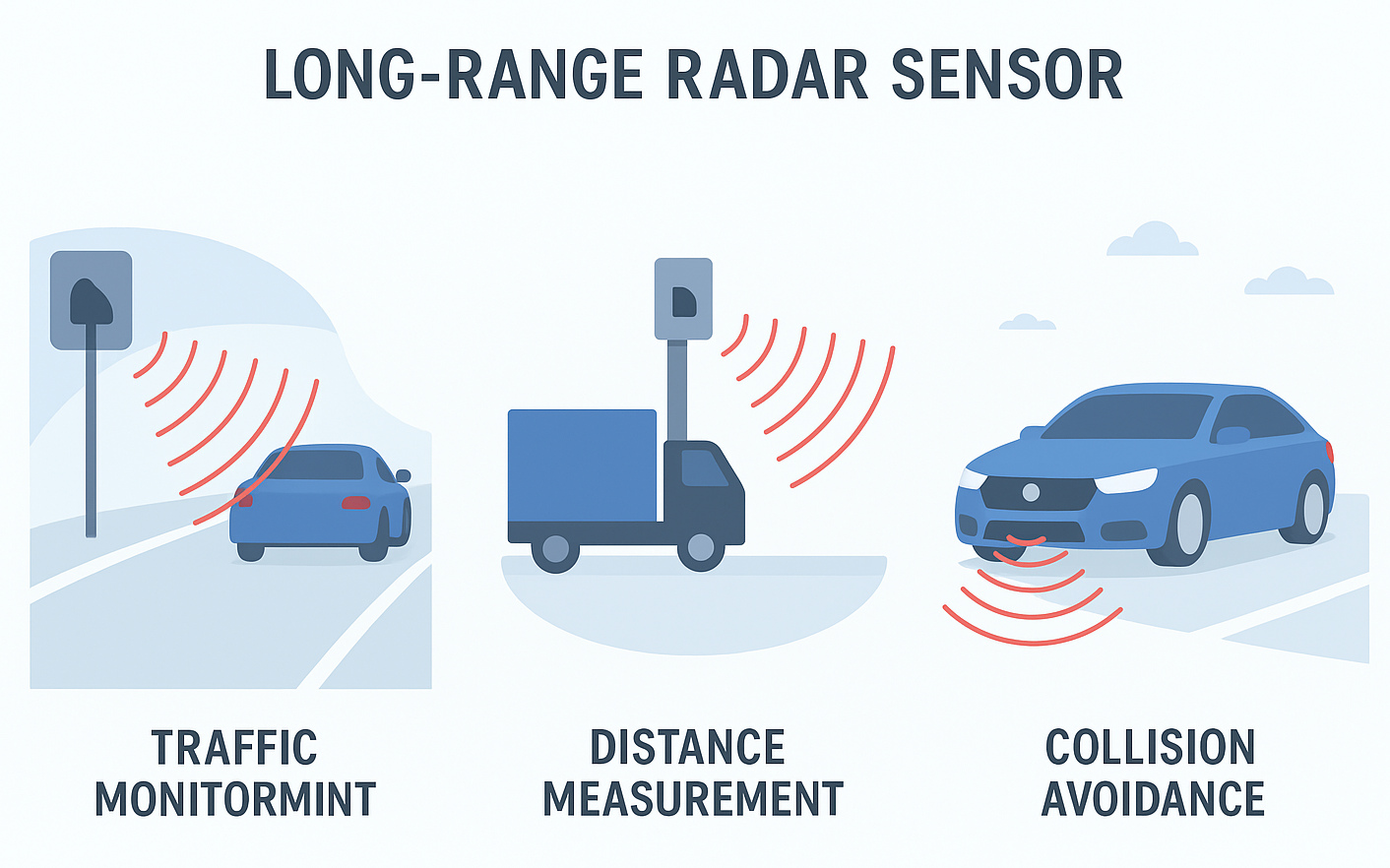
Modern cities face increasing challenges in traffic safety, congestion control, and accident prevention. To manage roads efficiently and safely, authorities and system integrators rely on Long Range Radar Sensors as the backbone of Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS).
1.1. Highway Speed Monitoring and Enforcement
On highways, Long Range Radar Sensors play a critical role in vehicle speed detection and tracking. They accurately measure vehicle velocity, distance, and trajectory — even across multiple lanes — regardless of weather or lighting.
Unlike traditional camera-based systems, radar technology remains effective during fog, heavy rain, or nighttime, ensuring uninterrupted operation. This reliability enables law enforcement and traffic agencies to detect over-speeding or dangerous driving behaviors under any condition.
1.2. Traffic Flow Analysis and Congestion Management
Radar sensors continuously monitor traffic density and vehicle behavior across wide areas. This real-time data allows transportation management systems to dynamically adjust signals, speed limits, or digital signage to prevent bottlenecks and reduce congestion.
For instance, when a radar detects a sudden slowdown in one lane, the system can trigger early warnings or reroute vehicles — minimizing the risk of rear-end collisions and improving traffic fluidity.
1.3. Accident Detection and Early Warning
In case of road incidents, radar sensors enable automatic incident detection by identifying stopped or slow-moving vehicles. Their long detection range allows early warnings to upstream drivers or traffic control centers, reducing secondary accidents and accelerating emergency response.
1.4. Smart Infrastructure Integration
As cities evolve toward smart mobility, Long Range Radar Sensors integrate seamlessly into V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) communication networks. They feed real-time environmental data into centralized systems, helping governments design safer roads and optimize traffic infrastructure.
By combining radar data with AI and cloud analytics, transportation agencies gain predictive insights — from identifying high-risk zones to predicting traffic patterns.
2. Perimeter Security and Area Protection
Beyond roadways, Long Range Radar Sensors are revolutionizing security and surveillance systems for critical infrastructure, industrial sites, and border control.
2.1. Reliable Intrusion Detection Across Large Areas
Traditional security systems often rely on video cameras or infrared detectors, both of which can fail under poor lighting or adverse weather. In contrast, radar sensors maintain full operational capability under fog, rain, dust, or complete darkness.
By transmitting electromagnetic waves and analyzing reflections, they detect any moving object — whether a person, vehicle, or drone — across vast distances, typically from 100 to 1000 meters. This allows for early threat detection and real-time tracking across large perimeters.
2.2. Smart Multi-Target Tracking and Classification
Modern Long Range Radar Sensors feature multi-target tracking capabilities, distinguishing between different types of objects based on motion patterns and radar signatures.
For example, in a large logistics facility, the system can differentiate between a human intruder, an authorized vehicle, or a stray animal — minimizing false alarms and improving operational efficiency.
2.3. Integration with Video and Alarm Systems
When integrated into a security management platform, radar sensors act as intelligent triggers. Once motion is detected, the system automatically cues PTZ cameras to zoom in on the precise location. This allows for visual verification before dispatching security personnel.
This radar-camera fusion enables proactive surveillance: instead of passively monitoring feeds, the system dynamically responds to events, ensuring faster and more accurate incident response.
2.4. Application Scenarios
Long Range Radar Sensors are increasingly deployed in:
-
Airports – to secure perimeters against unauthorized entry or drone intrusion.
-
Power plants and substations – to detect approaching threats before they reach the fence line.
-
Border areas and military facilities – to enable wide-area situational awareness.
-
Industrial parks and warehouses – to automate 24/7 site security and reduce manual patrols.
These use cases demonstrate how radar systems deliver cost-efficient, scalable, and always-on protection, even in the harshest environments.
3. Autonomous Driving and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Perhaps the most transformative use of Long Range Radar Sensors is in autonomous vehicles and ADAS. In this domain, radar is not just a sensor — it’s a core enabler of vehicle intelligence and safety.
3.1. Long-Range Detection for Safe Navigation
Autonomous vehicles require constant awareness of their surroundings to navigate safely at high speeds. Long Range Radar Sensors can detect vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles hundreds of meters ahead, giving the car’s control system sufficient time to react.
For example, a radar can spot a slowing truck 250 meters away — long before a camera or LiDAR system can confirm it visually — enabling early braking and smoother lane adjustments.
3.2. All-Weather Reliability
Unlike LiDAR or cameras, radar is unaffected by rain, fog, glare, or darkness. This makes it a critical sensing modality for ensuring consistent safety in all driving conditions. Even during storms or in tunnels, radar continues to provide accurate range, speed, and angle data.
3.3. Multi-Layer Sensing for Enhanced Decision-Making
In ADAS and autonomous driving, radar sensors are typically combined with short-range radar, cameras, and LiDAR to form a multi-layer perception system.
Long Range Radar provides forward-looking coverage for adaptive cruise control, collision avoidance, and emergency braking systems, while short-range radar handles blind spot monitoring and parking assistance.
Together, they enable features such as:
-
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) – maintaining safe distance from vehicles ahead.
-
Forward Collision Warning (FCW) – identifying potential collisions and issuing alerts.
-
Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB) – automatically stopping the vehicle to avoid crashes.
-
Highway Pilot Mode – allowing semi-autonomous driving at high speeds with full awareness of nearby traffic.
3.4. Enabling Future Mobility
As the automotive industry advances toward full autonomy, Long Range Radar Sensors are evolving to support high-resolution 4D imaging radar. These next-generation systems capture not only distance and speed but also object height and shape — enhancing the vehicle’s understanding of complex environments.
With their low power consumption, affordability, and robust performance, radar sensors are becoming a foundational element in safe, scalable autonomous mobility.
4. The Advantages that Define Long Range Radar Sensors
Across all these industries, Long Range Radar Sensors stand out due to their unique combination of benefits:
-
Extended Detection Range – Identify and track objects hundreds of meters away.
-
All-Weather Performance – Operate seamlessly through rain, fog, dust, and darkness.
-
High Reliability – Maintain accuracy in the most demanding conditions.
-
Real-Time Tracking – Monitor multiple moving targets simultaneously.
-
Scalability and Integration – Easily connect to existing control, security, or automation systems.
-
Low Maintenance – Durable and designed for continuous operation in harsh environments.
These characteristics make radar technology a preferred choice for applications that demand continuous awareness and rapid response.
5. Conclusion: The Backbone of a Safer, Smarter World
From smart highways and secured borders to autonomous vehicles, Long Range Radar Sensors are redefining how humans and machines interact with the environment. They solve practical problems — detecting dangers earlier, guiding vehicles more safely, and safeguarding assets around the clock.
In transportation, they reduce accidents and optimize traffic flow.
In security, they create intelligent, scalable defense systems.
In autonomous driving, they empower vehicles to perceive and respond like humans — but faster and safer.