3D Radar Technology for Traffic and Security Applications
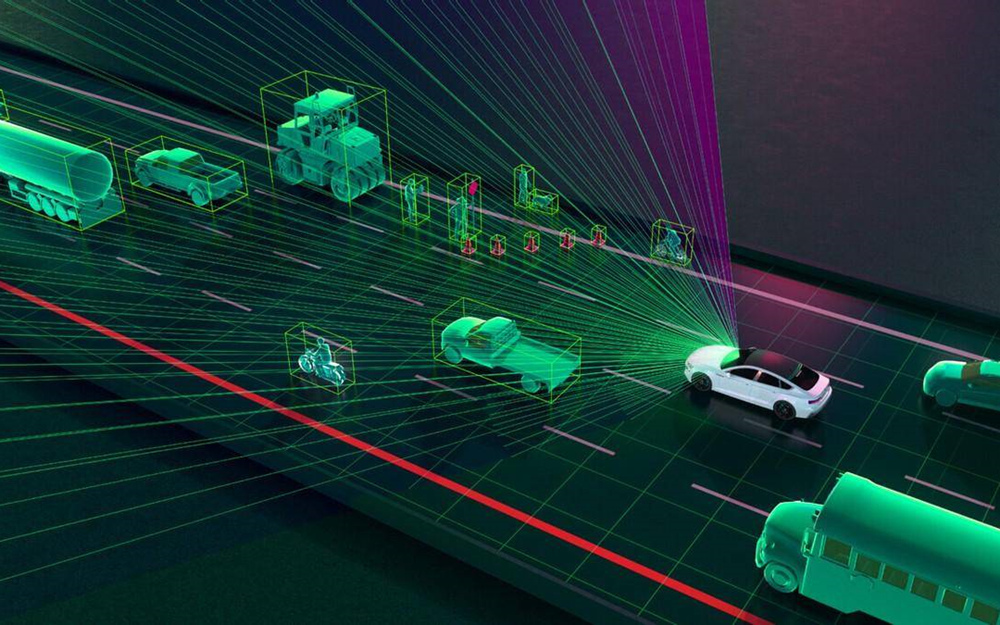
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving world, radar technology plays a critical role across various industries, particularly in transportation and security. Among the numerous types of radar, 3D radar stands out due to its advanced capability to provide detailed spatial information, enabling enhanced detection, tracking, and monitoring of objects in three dimensions. This article delves deep into 3D radar technology, focusing on its applications in traffic and security systems, benefits, types, and the latest trends shaping this transformative technology.
What is 3D Radar?
3D radar is a sophisticated radar system that can detect and measure the position of objects in three spatial dimensions: range, azimuth (horizontal angle), and elevation (vertical angle). Unlike traditional 2D radar, which provides information primarily about range and bearing, 3D radar delivers a complete spatial map of targets, allowing for precise identification and tracking of their location and movement.
Key Components of 3D Radar Systems
- Transmitter: Sends out radio waves toward the target.
- Receiver: Captures the reflected signals from objects.
- Signal Processor: Analyzes the received data to extract 3D positional information.
- Display & Control Unit: Visualizes data for operators and integrates with other systems.
Why 3D Radar is Crucial in Traffic and Security Industries
Enhanced Situational Awareness
3D radar provides a comprehensive picture of the environment, enabling operators to detect objects with greater accuracy and detail. This is vital for monitoring traffic flow, detecting obstacles, and identifying potential security threats.
Improved Object Detection and Classification
With elevation data, 3D radar can distinguish between objects at different heights, such as differentiating a pedestrian from a vehicle or a drone from a bird. This capability reduces false alarms and increases reliability in security systems.
All-Weather, Day-Night Operation
Unlike optical systems, 3D radar works effectively in adverse weather conditions such as fog, rain, or snow, and operates reliably during both day and night, ensuring continuous monitoring.
Applications of 3D Radar in Traffic Systems
1. Traffic Monitoring and Management
3D radar systems monitor real-time traffic flow on roads and highways by detecting vehicles’ position, speed, and direction. This data helps traffic management centers optimize signal timings, reduce congestion, and improve road safety.
2. Autonomous and Connected Vehicles
3D radar sensors are integral components in autonomous vehicles, offering high-resolution environmental mapping to detect obstacles, other vehicles, and pedestrians. This helps in navigation, collision avoidance, and adaptive cruise control.
3. Speed Enforcement and Red Light Cameras
3D radar enables precise speed measurement and vehicle classification, which improves the effectiveness of automated enforcement systems such as speed cameras and red light monitoring.
4. Toll Collection and Vehicle Classification
By accurately detecting vehicle dimensions and types, 3D radar supports automatic toll collection systems and traffic analytics, facilitating smooth toll plaza operations and road usage analysis.
Applications of 3D Radar in Security and Surveillance
1. Perimeter Security
3D radar systems provide real-time monitoring of a secured perimeter by detecting and tracking intruders or unauthorized vehicles, even in low visibility conditions.
2. Airport and Harbor Surveillance
Airports and seaports use 3D radar to monitor aircraft, ships, and ground vehicles to ensure safety, prevent unauthorized access, and support operational efficiency.
3. Drone Detection and Countermeasures
With the rise of drone-related security threats, 3D radar is increasingly utilized to detect, track, and classify drones by their flight path and altitude, enabling timely intervention.
4. Urban Security and Critical Infrastructure Protection
3D radar systems enhance security around critical infrastructure such as power plants, government buildings, and public spaces by detecting suspicious activities and providing detailed situational awareness.
Technical Advantages of 3D Radar Over Traditional Systems
| Feature | 2D Radar | 3D Radar |
|---|---|---|
| Spatial Information | Range & Azimuth | Range, Azimuth & Elevation |
| Object Differentiation | Limited | High (Height & Shape Info) |
| False Alarm Reduction | Moderate | Significantly Reduced |
| Environmental Adaptability | Good | Excellent |
| Integration with AI & ML | Possible | Highly Effective |
Types of 3D Radar Systems
Phased Array Radar
Uses electronically steered antenna beams to rapidly scan the environment in 3D. Widely used in defense, traffic control, and advanced security systems.
Mechanical 3D Radar
Employs rotating antennas combined with elevation scanning mechanisms to build a 3D image. Often used in air traffic control and weather monitoring.
MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) 3D Radar
Utilizes multiple transmitting and receiving antennas to improve spatial resolution and detection accuracy. Increasingly popular in automotive radar and urban surveillance.
Latest Trends and Innovations in 3D Radar Technology
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Modern 3D radar systems incorporate AI algorithms to enhance target recognition, anomaly detection, and predictive analytics, enabling smarter traffic and security management.
Miniaturization and Cost Reduction
Advancements in semiconductor and antenna design are making 3D radar sensors smaller, more affordable, and easier to deploy in various applications, from vehicles to portable security devices.
Fusion with Other Sensors
Combining 3D radar with LiDAR, cameras, and infrared sensors creates multi-sensor platforms that offer superior accuracy and robustness for complex environments.
5G and IoT Connectivity
3D radar systems are increasingly integrated with 5G networks and IoT platforms, allowing real-time data sharing, remote monitoring, and cloud-based analytics.
Choosing the Right 3D Radar for Your Needs
When selecting a 3D radar system for traffic or security applications, consider:
- Detection Range: Ensure the radar covers the required operational area.
- Resolution and Accuracy: Higher resolution is critical for detailed object classification.
- Environmental Conditions: Choose models designed for local weather and terrain.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure compatibility with existing control systems and data platforms.
- Cost and Scalability: Balance initial investment with long-term operational benefits.
Case Studies of 3D Radar in Action
Smart City Traffic Management
A metropolitan city deployed 3D radar at key intersections to monitor vehicular and pedestrian traffic. This enabled adaptive traffic signals that reduced congestion by 30% and improved emergency vehicle response times.
Airport Perimeter Security Enhancement
An international airport integrated 3D radar systems along its perimeter fence. The system detected low-flying drones and unauthorized personnel, preventing several security breaches and improving overall safety.
Conclusion
3D radar technology is revolutionizing the fields of traffic management and security surveillance by providing detailed, accurate, and reliable three-dimensional spatial data. Its ability to operate in diverse environmental conditions, combined with advancements in AI and sensor fusion, makes it an indispensable tool for modern infrastructure and safety systems.
As a leading supplier of advanced traffic and security radar solutions, we are committed to helping you leverage the power of 3D radar to enhance operational efficiency, safety, and situational awareness. Contact us today to explore our state-of-the-art 3D radar products tailored to your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How does 3D radar improve traffic safety?
A1: By providing precise 3D data on vehicle positions and movements, 3D radar helps detect potential collisions, monitor traffic flow, and enable smart traffic control systems.
A1: By providing precise 3D data on vehicle positions and movements, 3D radar helps detect potential collisions, monitor traffic flow, and enable smart traffic control systems.
Q2: Can 3D radar detect drones?
A2: Yes, 3D radar can detect, track, and classify drones by analyzing their spatial position and flight patterns, making it effective for drone threat mitigation.
A2: Yes, 3D radar can detect, track, and classify drones by analyzing their spatial position and flight patterns, making it effective for drone threat mitigation.
Q3: Is 3D radar affected by weather conditions?
A3: 3D radar operates efficiently in various weather conditions such as fog, rain, and darkness, unlike optical sensors which may be limited.
A3: 3D radar operates efficiently in various weather conditions such as fog, rain, and darkness, unlike optical sensors which may be limited.
Q4: What industries benefit most from 3D radar?
A4: Transportation, security, defense, aerospace, and critical infrastructure protection are primary industries leveraging 3D radar technology.
A4: Transportation, security, defense, aerospace, and critical infrastructure protection are primary industries leveraging 3D radar technology.
Recent Posts
- Traffic Enforcement: How Radar Technology Solves Real-World Road Safety Challenges
- Security Radar Isn’t Just Another Sensor—It’s Your First Line of Truth
- Wavetronix SmartSensor: Transforming Traffic Management with Intelligent Radar Technology
- Speed Enforcement Solutions: Precision, Performance, and Multi-Lane Control with Next-Generation Radar Technology
- Unlocking Precision and Safety with Long Range Radar Sensor
- 4D Radar: The Next Evolution in Intelligent Sensing for Traffic and Security Applications
- Radar Sensors: Practical Solutions for Traffic and Security Challenges
